APRIL
Month of Devotion to the Blessed Sacrament

V. O Sacrament Most Holy, O Sacrament Divine,
R. All praise and all thanksgiving be every moment Thine.
______________________________________________
Dominica II Post Pascha
Second Sunday after Easter
The Good Shepherd
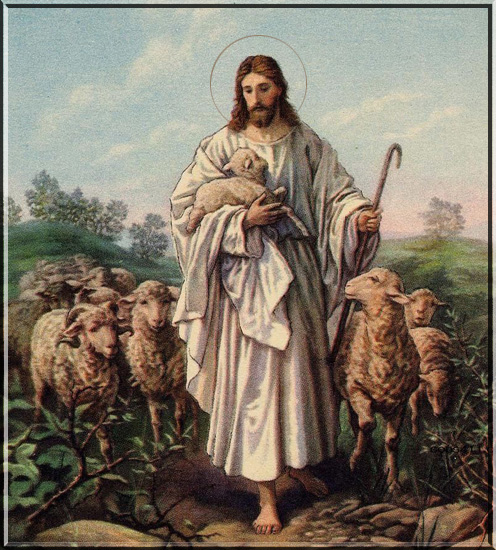

I am the Good Shepherd. The Good Shepherd giveth His life for His sheep. ~Jn. 10: 11
Sancta Missa ~ The Holy Mass
Introit
Ps. 32: 5-6
The earth is full of the goodness of the Lord, alleluia: by the word of the Lord were the heavens made, alleluia, alleluia.
Ps. 32: 1
Rejoice in the Lord, O ye righteous: praise is comely for the upright.
V. Glory be to the Father, and to the Son, and to the Holy Ghost.
R. As it was in the beginning, is now, and ever shall be, world without end. Amen.
The earth is full of the goodness of the Lord, alleluia: by the word of the Lord were the heavens made, alleluia, alleluia.
Collect
Let us pray.
O God, who, by the humility of Thy Son, didst lift up a fallen world, grant unending happiness to Thy faithful: that those whom Thou hast snatched from the perils of endless death, Thou mayest cause to rejoice in everlasting days.
Through the same Jesus Christ, thy Son, Our Lord, Who liveth and reigneth with thee in the unity of the Holy Ghost, God, world without end.
R. Amen.
Lesson
Lesson from the first letter of St. Peter the Apostle
1 Pet. 2: 21-25
Dearly beloved, Christ suffered for us, leaving you an example, that you should follow His steps who did no sin, neither was guile found in His mouth. Who when He was reviled, did not revile: when He suffered, He threatened not, but delivered Himself to him that judged Him unjustly: who His own self bore our sins in His body upon the tree: that we, being dead to sins, should live to justice; by whose stripes you were healed. For you were as sheep going astray: but you are now converted to the Shepherd and Bishop of your souls.
R. Thanks be to God.
Alleluia
Allelúja, allelúja.
Luke 24: 35
The disciples knew the Lord Jesus in the breaking of bread. Allelúja.
John 10: 14
I am the good Shepherd: and I know My sheep, and Mine know Me. Allelúja.
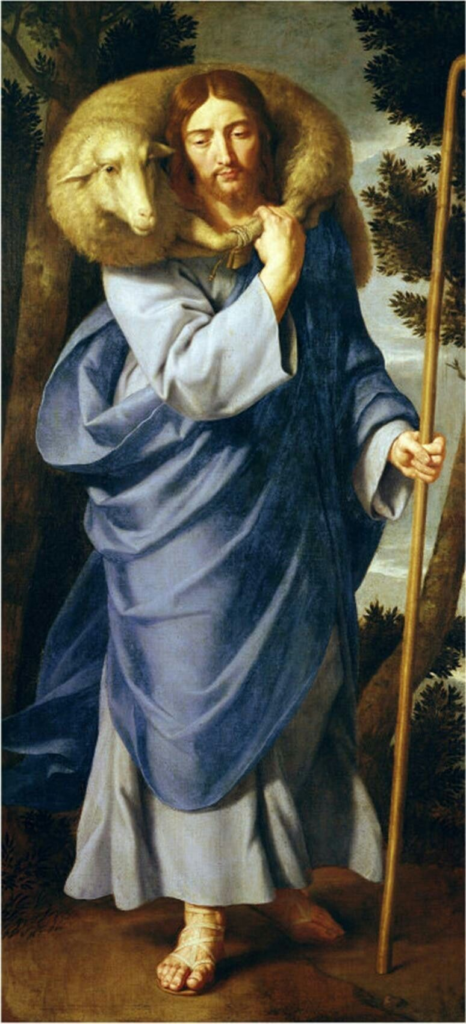

I am the Good Shepherd; and I know Mine, and Mine know Me. ~Jn. 10: 14
Gospel
Continuation ✠ of the Holy Gospel according to John
John 10: 11-16
At that time Jesus said to the Pharisees: I am the Good Shepherd. The Good Shepherd giveth His life for His sheep. But the hireling, and he that is not the shepherd, whose own the sheep are not, seeth the wolf coming and leaveth the sheep and flieth: and the wolf catcheth and scattereth the sheep: and the hireling flieth, because he is a hireling, and he hath no care for the sheep. I am the good Shepherd: and I know Mine, and Mine know Me, as the Father knoweth Me, and I know the Father: and I lay down My life for My sheep. And other sheep I have that are not of this fold: them also I must bring, and they shall hear My voice, and there shall be one fold and one shepherd.
R. Praise be to Thee, O Christ.
Offertory
Let us pray.
Ps. 62: 2; 62: 5
O God, my God, to Thee do I watch at break of day: and in Thy Name I will lift up my hands, allelúja.
Secret
May this holy offering, O Lord, always bring to us Thy healing blessing: that what it represents in a Mystery, it may accomplish with power.
Through Jesus Christ, thy Son our Lord, Who liveth and reigneth with thee, in the unity of the Holy Ghost, God, world without end.
R. Amen.
Preface
Easter
It is truly meet and just, right and for our salvation, at all times to praise Thee, O Lord, but more gloriously especially on this day when Christ our Pasch was sacrificed. For He is the Lamb Who hath taken away the sins of the world: Who by dying hath destroyed our death: and by rising again hath restored us to life. And therefore with Angels and Archangels, with Thrones and Dominations, and with all the hosts of the heavenly army, we sing the hymn of Thy glory, evermore saying:
Holy, Holy, Holy, Lord God of Sabaoth! Heaven and earth are full of Thy glory! Hosanna in the highest! Blessed is He that cometh in the Name of the Lord! Hosanna in the highest!
Communion
John 10: 14
I am the Good Shepherd, alleluia: and I know My sheep, and Mine know Me, allelúja, allelúja.
Post Communion
Let us pray.
Grant unto us, we beseech Thee, almighty God, that having received the grace of a new life, we may ever glory in Thy gift.
Through Jesus Christ, thy Son our Lord, Who liveth and reigneth with thee, in the unity of the Holy Ghost, God, world without end.
R. Amen.
*********************
Feed My lambs … Feed My lambs … Feed My sheep!
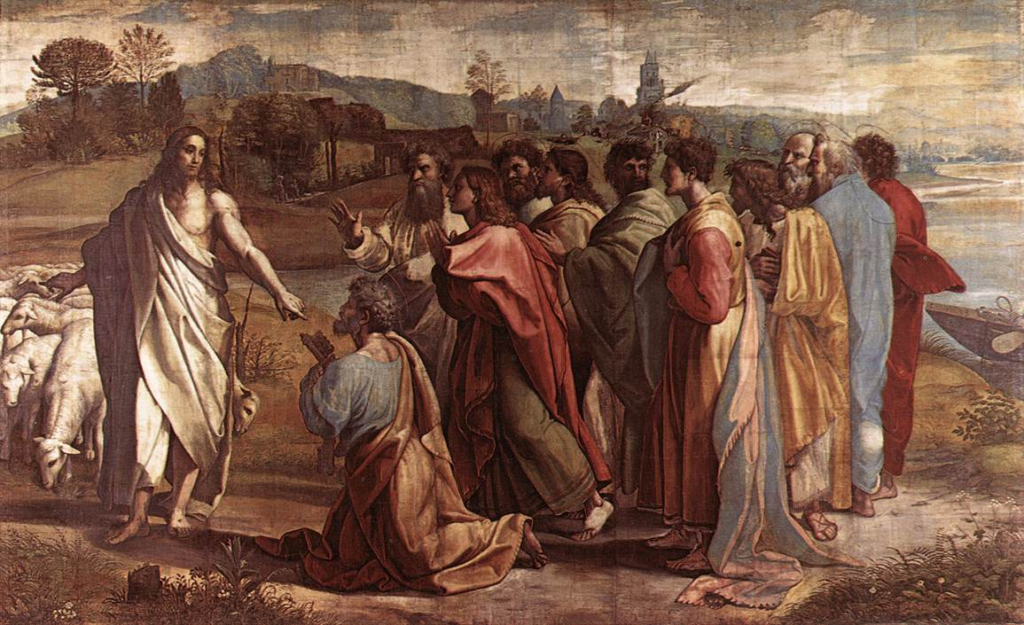

This Sunday goes under the name Good Shepherd Sunday, because in the Mass there is read the Gospel of St. John, wherein our Lord calls Himself by this name. How very appropriate is this passage of this Gospel to the present season, when our divine Master began His work of establishing and consolidating the Church, by giving it the pastor, or shepherd, who was to govern it to the end of time! In accordance with the eternal decree, the Man-God, on the fortieth day after His Resurrection, is to withdraw His visible presence from the world. He is not to be seen again upon the earth until the last day, when He will come again to judge the living and the dead. And yet He could never abandon mankind, for which He offered Himself on the Cross, and delivered from death and hell by rising triumphantly from the grave. He will continue to be its Head after His Ascension into heaven: but what shall we have on earth to supply His place? We shall have the Church. It is to the Church that He will leave all his own authority to rule us; it is into the hands of the Church that He will entrust all the truths He has taught; it is the Church that He will make the dispenser of all those means of salvation which He has destined for the world. This Church is a society, unto which all mankind is invited. It is composed of two classes of members; the governing and the governed; the teaching and the taught; the sanctifying and the sanctified. This society is the Spouse of Christ; it is by her that He produces His elect. She is the one only Mother of the elect; out of her bosom there is no salvation. But how is this society to subsist? How is it to persevere through the long ages of time, even to the last day? Who is to give it unity and adhesion of its parts? What is to be the visible link between its members—the palpable sign of its being the true Spouse of Christ, in the event of other societies rising up and disputing her titles? If JesusHimself could have remained with us we should have had nothing to fear, for where He is, there also are truth and life; but, as He says, He is going, and we may not as yet follow Him. Give ear, then, and learn what is the primary quality of the true Spouse of Christ. Jesus was one day, previous to his Passion, in the country of Cæsarea Philippi, His Apostles standing around Him, and He began questioning them about what they thought of Him. One of them, Simon the son of John or Jonas, and brother to Andrew, answered in the name of all, and said: Thou art Christ, the Son of the living God! Jesus expressed His pleasure at receiving Simon’s testimony, which was not the result of any human knowledge, but the expression of a divine revelation there and then granted to him; and He immediately told this Apostle that from that time forward he was to be, not Simon, but Peter (which means a rock). Christ had been spoken of by the prophets under the name of a Rock, or Stone [Is. 28: 16]; by thus solemnly conferring upon His disciple a title so characteristically that of the Messias, Jesus would give us to understand that Simon was to have something in common with Himself which the other Apostles were not to have. After saying to him: Thou art Peter (that is, thou art the rock), He added: And upon this rock I will build My Church. Let us weigh the force of these words of the Son of God. He has a project in view: He intends to build a Church. It is not now that He will build it, but at some future period; but one thing we already know as a certainty— that this Church will be built on Peter. That future is now become the present. We are come to the last days of Jesus’ visible presence here below. The time is come for Him to make good His promise, and found the kingdom of God—that Church which He was to build upon the earth.… He suddenly addresses Himself to Peter: Simon, son of John, lovest thou Me? Peter, with his usual eagerness, answers his Master’s question: Yea, Lord, Thou knowest that I love Thee. Jesus resumes, with a tone of authority: Feed My lambs … Feed My lambs … Feed My sheep ! Here, then, we have Peter made shepherd by Him who says of Himself: I am the Good Shepherd. Firstly, our Lord gives His Apostle, twice over, the care of His lambs; this does not make him the complete shepherd: but when He bids him feed His sheep too, the whole flock is subjected to his authority. Now, therefore, let the Church show herself, let her take her stand, let her spread herself through the length and breadth of the nations; Simon, the son of John, is proclaimed its visible head.
~ Commentary from The Liturgical Year by Fr. Prosper Guéranger O.S.B. (1805-1875).
_______________________________________________________________________
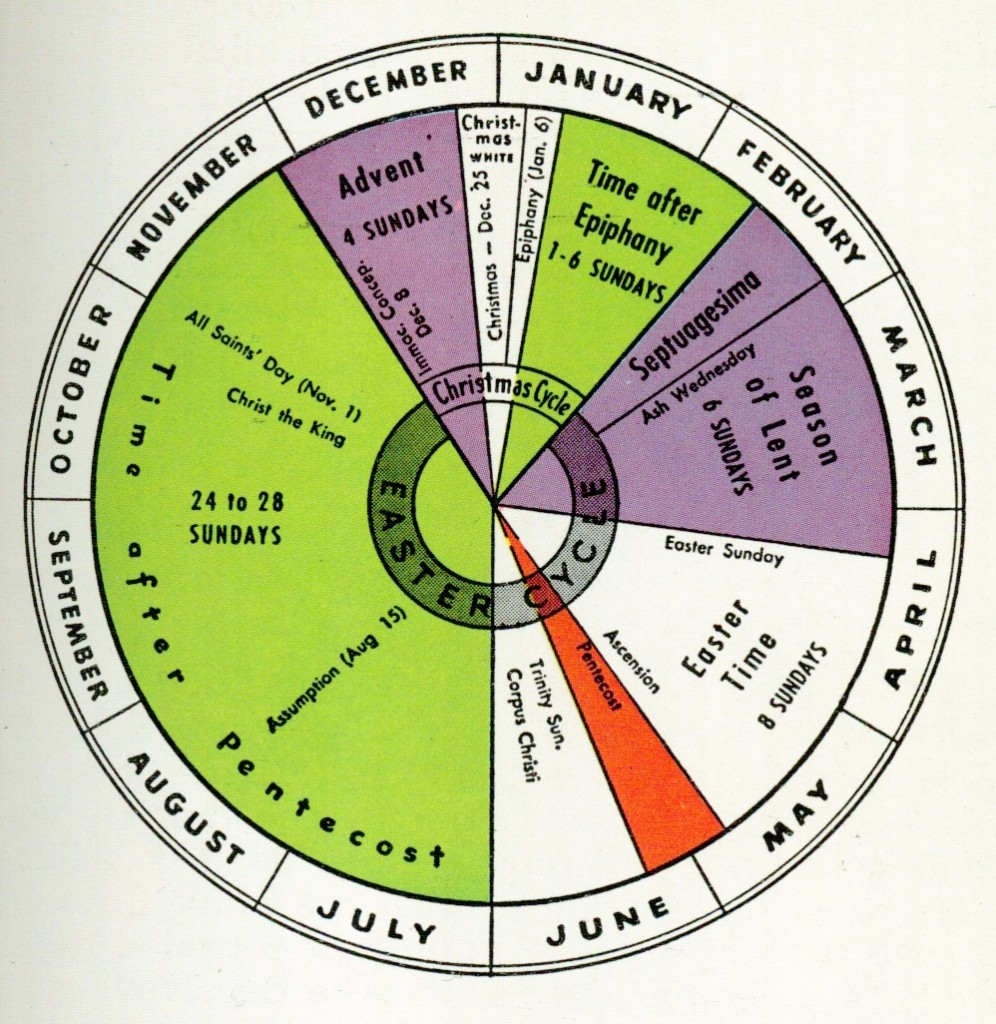
The Liturgical Year
_____________________________________________________________________
The Holy & Blessed Trinity

Baltimore Catechism #3
LESSON 3: ON THE UNITY AND TRINITY OF GOD
Q. 180. What does “unity,” and what does “trinity” mean?
A. “Unity” means being one, and “trinity” means three-fold or three in one.
Q. 181. Can we find an example to fully illustrate the mystery of the Blessed Trinity?
A. We cannot find an example to fully illustrate the mystery of the Blessed Trinity, because the mysteries of our holy religion are beyond comparison.
Q. 182. Is there but one God?
A. Yes; there is but one God.
Q. 183. Why can there be but one God?
A. There can be but one God because God, being supreme and infinite, cannot have an equal.
Q. 184. What does “supreme” mean?
A. “Supreme” means the highest in authority; also the most excellent or greatest possible in anything. Thus in all things God is supreme, and in the Church the Pope is supreme.
Q. 185. When are two persons said to be equal?
A. Two persons are said to be equal when one is in no way greater than or inferior to the other.
Q. 186. How many persons are there in God?
A. In God there are three Divine persons, really distinct, and equal in all things –the Father, the Son, and the Holy Ghost.
Q. 187. What do “divine” and “distinct” mean?
A. “Divine” means pertaining to God, and “distinct” means separate; that is, not confounded or mixed with any other thing.
Q. 188. Is the Father God?
A. The Father is God and the first Person of the Blessed Trinity.
Q. 189. Is the Son God?
A. The Son is God and the second Person of the Blessed Trinity.
Q. 190. Is the Holy Ghost God?
A. The Holy Ghost is God and the third Person of the Blessed Trinity.
Q. 191. Do “first,” “second,” and “third” with regard to the persons of the Blessed Trinity mean that one person existed before the other or that one is greater than the other?
A. “First,” “second,” and “third” with regard to the persons of the Blessed Trinity do not mean that one person was before the other or that one is greater than the other; for all the persons of the Trinity are eternal and equal in every respect. These numbers are used to mark the distinction between the persons, and they show the order in which the one proceeded from the other.

Q. 192. What do you mean by the Blessed Trinity?
A. By the Blessed Trinity I mean one God in three Divine Persons.
Q. 193. Are the three Divine Persons equal in all things?
A. The three Divine Persons are equal in all things.
Q. 194. Are the three Divine Persons one and the same God?
A. The three Divine Persons are one and the same God, having one and the same Divine nature and substance.
Q. 195. What do we mean by the “nature” and “substance” of a thing?
A. By the “nature” of a thing we mean the combination of all the qualities that make the thing what it is. By the “substance” of a thing we mean the part that never changes, and which cannot be changed without destroying the nature of the thing.
Q. 196. Can we fully understand how the three Divine Persons are one and the same God?
A. We cannot fully understand how the three Divine Persons are one and the same God, because this is a mystery.
Q. 197. What is a mystery?
A. A mystery is a truth which we cannot fully understand.
Q. 198. Is every truth which we cannot understand a mystery?
A. Every truth which we cannot understand is not a mystery; but every revealed truth which no one can understand is a mystery.
Q. 199. Should we believe truths which we cannot understand?
A. We should and often do believe truths which we cannot understand when we have proof of their existence.
Q. 200. Give an example of truths which all believe, though many do not understand them.
A. All believe that a seed planted in the ground will produce a flower or tree often with more than a thousand other seeds equal to itself, though many cannot understand how this is done.
Q. 201. Why must a divine religion have mysteries?
A. A divine religion must have mysteries because it must have supernatural truths and God Himself must teach them. A religion that has only natural truths, such as man can know by reason alone, fully understand and teach, is only a human religion.
Q. 202. Why does God require us to believe mysteries?
A. God requires us to believe mysteries that we may submit our understanding to Him.
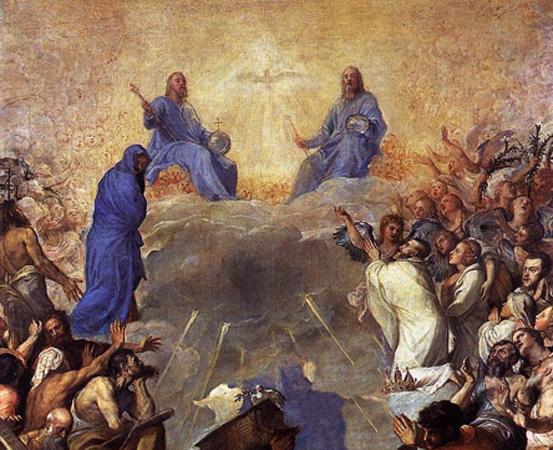

Q. 203. By what form of prayer do we praise the Holy Trinity?
A. We praise the Holy Trinity by a form of prayer called the Doxology, which has come down to us almost from the time of the Apostles.
Q. 204. Say the Doxology.
A. The Doxology is: “Glory be to the Father, and to the Son, and to the Holy Ghost. As it was in the beginning, is now, and ever shall be, world without end. Amen.”
Q. 205. Is there any other form of the Doxology?
A. There is another form of the Doxology, which is said in the celebration of the Mass. It is called the “Gloria in excelsis” or “Glory be to God on high,” etc., the words sung by the Angels at the birth of Our Lord.
_____________________________________________________________________
The Holy & Blessed Eucharist
Baltimore Catechism #3
LESSON 22: ON THE HOLY EUCHARIST
Q. 869. What does the word Eucharist strictly mean?
A. The word Eucharist strictly means pleasing, and this Sacrament is so called because it renders us most pleasing to God by the grace it imparts, and it gives us the best means of thanking Him for all His blessings.
Q. 870. What is the Holy Eucharist?
A. The Holy Eucharist is the Sacrament which contains the body and blood, soul and divinity, of our Lord Jesus Christ under the appearances of bread and wine.
Q. 871. What do we mean when we say the Sacrament which contains the Body and Blood?
A. When we say the Sacrament which contains the Body and Blood, we mean the Sacrament which is the Body and Blood, for after the Consecration there is no other substance present in the Eucharist.
Q. 872. When is the Holy Eucharist a Sacrament, and when is it a sacrifice?
A. The Holy Eucharist is a Sacrament when we receive it in Holy Communion and when it remains in the Tabernacle of the Altar. It is a sacrifice when it is offered up at Mass by the separate Consecration of the bread and wine, which signifies the separation of Our Lord’s blood from His body when He died on the Cross.
Q. 873. When did Christ institute the Holy Eucharist?
A. Christ instituted the Holy Eucharist at the Last Supper, the night before He died.
Q. 874. Who were present when our Lord instituted the Holy Eucharist?
A. When Our Lord instituted the Holy Eucharist, the twelve Apostles were present.
Q. 875. How did our Lord institute the Holy Eucharist?
A. Our Lord instituted the Holy Eucharist by taking bread, blessing, breaking, and giving to His Apostles, saying: “Take ye and eat. This is my body”; and then, by taking the cup of wine, blessing and giving it, saying to them: “Drink ye all of this. This is my blood which shall be shed for the remission of sins. Do this for a commemoration of me.”
Q. 876. What happened when our Lord said, “This is my body; this is my blood”?
A. When Our Lord said, “This is my body,” the substance of the bread was changed into the substance of His body; when He said, “This is my blood,” the substance of the wine was changed into the substance of His blood.
Q. 877. How do we prove the Real Presence, that is, that Our Lord is really and truly present in the Holy Eucharist?
A. We prove the Real Presence — that is, that Our Lord is really and truly present in the Holy Eucharist:
1. By showing that it is possible to change one substance into another;
2. By showing that Christ did change the substance of bread and wine into the substance of His body and blood;
3. By showing that He gave this power also to His Apostles and to the priests of His Church.

Q. 878. How do we know that it is possible to change one substance into another?
A. We know that it is possible to change one substance into another, because:
1. God changed water into blood during the plagues of Egypt.
2. Christ changed water into wine at the marriage of Cana.
3. Our own food is daily changed into the substance of our flesh and blood; and what God does gradually, He can also do instantly by an act of His will.
Q. 879. Are these changes exactly the same as the changes that take place in the Holy Eucharist?
A. These changes are not exactly the same as the changes that take place in the Holy Eucharist, for in these changes the appearance also is changed, but in the Holy Eucharist only the substance is changed while the appearance remains the same.
Q. 880. How do we show that Christ did change bread and wine into the substance of His body and blood?
A. We show that Christ did change bread and wine into the substance of His body and blood:
1. From the words by which He promised the Holy Eucharist;
2. From the words by which He instituted the Holy Eucharist;
3. From the constant use of the Holy Eucharist in the Church since the time of the Apostles;
4. From the impossibility of denying the Real Presence in the Holy Eucharist, without likewise denying all that Christ has taught and done; for we have stronger proofs for the Holy Eucharist than for any other Christian truth.
Q. 881. Is Jesus Christ whole and entire both under the form of bread and under the form of wine?
A. Jesus Christ is whole and entire both under the form of bread and under the form of wine.
Q. 882. How do we know that under the appearance of bread we receive also Christ’s blood; and under the appearance of wine we receive also Christ’s body?
A. We know that under the appearance of bread we receive also Christ’s blood, and under the appearance of wine we receive also Christ’s body; because in the Holy Eucharist we receive the living body of Our Lord, and a living body cannot exist without blood, nor can living blood exist without a body.
Q. 883. Is Jesus Christ present whole and entire in the smallest portion of the Holy Eucharist, under the form of either bread or wine?
A. Jesus Christ is present whole and entire in the smallest portion of the Holy Eucharist under the form of either bread or wine; for His body in the Eucharist is in a glorified state, and as it partakes of the character of a spiritual substance, it requires no definite size or shape.
Q. 884. Did anything remain of the bread and wine after their substance had been changed into the substance of the body and blood of our Lord?
A. After the substance of the bread and wine had been changed into the substance of the body and blood of Our Lord, there remained only the appearances of bread and wine.
Q. 885. What do you mean by the appearances of bread and wine?
A. By the appearances of bread and wine I mean the figure, the color, the taste, and whatever appears to the senses.
Q. 886. What is this change of the bread and wine into the body and blood of our Lord called?
A. This change of the bread and wine into the body and blood of Our Lord is called Transubstantiation.
Q. 887. What is the second great miracle in the Holy Eucharist?
A. The second great miracle in the Holy Eucharist is the multiplication of the presence of Our Lord’s body in so many places at the same time, while the body itself is not multiplied — for there is but one body of Christ.
Q. 888. Are there not, then, as many bodies of Christ as there are tabernacles in the world, or as there are Masses being said at the same time?
A. There are not as many bodies of Christ as there are tabernacles in the world, or as there are Masses being said at the same time; but only one body of Christ, which is everywhere present whole and entire in the Holy Eucharist, as God is everywhere present, while He is but one God.

Q. 889. How was the substance of the bread and wine changed into the substance of the body and blood of Christ?
A. The substance of the bread and wine was changed into the substance of the body and blood of Christ by His almighty power.
Q. 890. Does this change of bread and wine into the body and blood of Christ continue to be made in the Church?
A. This change of bread and wine into the body and blood of Christ continues to be made in the Church by Jesus Christ through the ministry of His priests.
Q. 891. When did Christ give His priests the power to change bread and wine into His body and blood?
A. Christ gave His priests the power to change bread and wine into His body and blood when He said to the Apostles, “Do this in commemoration of Me.”
Q. 892. What do the words “Do this in commemoration of Me” mean?
A. The words “Do this in commemoration of Me” mean: Do what I, Christ, am doing at My last supper, namely, changing the substance of bread and wine into the substance of My body and blood; and do it in remembrance of Me.
Q. 893. How do the priests exercise this power of changing bread and wine into the body and blood of Christ?
A. The priests exercise this power of changing bread and wine into the body and blood of Christ through the words of consecration in the Mass, which are words of Christ: “This is my body; this is my blood.”
Q. 894. At what part of the Mass does the Consecration take place?
A. The Consecration in the Mass takes place immediately before the elevation of the Host and Chalice, which are raised above the head of the priest that the people may adore Our Lord who has just come to the altar at the words of Consecration.
_____________________________________________________________________
The Holy Sacrifice of the Mass

Baltimore Catechism #3
LESSON 24: ON THE HOLY SACRIFICE OF THE MASS
Q. 916. When and where are the bread and wine changed into the body and blood of Christ?
A. The bread and wine are changed into the body and blood of Christ at the Consecration in the Mass.
Q. 917. What is the Mass?
A. The Mass is the unbloody sacrifice of the body and blood of Christ.
Q. 918. Why is this Sacrifice called the Mass?
A. This Sacrifice is called the “Mass” very probably from the words “Ite Missa est,” used by the priest as he tells the people to depart when the Holy Sacrifice is ended.
Q. 919. What is a sacrifice?
A. A sacrifice is the offering of an object by a priest to God alone, and the consuming of it to acknowledge that He is the Creator and Lord of all things.
Q. 920. Is the Mass the same sacrifice as that of the Cross?
A. The Mass is the same sacrifice as that of the Cross.
Q. 921. How is the Mass the same sacrifice as that of the Cross?
A. The Mass is the same sacrifice as that of the Cross because the offering and the priest are the same — Christ our Blessed Lord; and the ends for which the sacrifice of the Mass is offered are the same as those of the sacrifice of the Cross.
Q. 922. What were the ends for which the sacrifice of the Cross was offered?
A. The ends for which the sacrifice of the Cross was offered were:
1. To honour and glorify God;
2. To thank Him for all the graces bestowed on the whole world;
3. To satisfy God’s justice for the sins of men;
4. To obtain all graces and blessings.

Q. 923. How are the fruits of the Mass distributed?
A. The fruits of the Mass are distributed thus:
1. The first benefit is bestowed on the priest who says the Mass;
2. The second on the person for whom the Mass is said, or for the intention for which it is said;
3. The third on those who are present at the Mass, and particularly on those who serve it, and
4. The fourth on all the faithful who are in communion with the Church.
Q. 924. Are all Masses of equal value in themselves or do they differ in worth?
A. All Masses are equal in value in themselves and do not differ in worth, but only in the solemnity with which they are celebrated or in the end for which they are offered.
Q. 925. How are Masses distinguished?
A. Masses are distinguished thus:
1. When the Mass is sung by a bishop, assisted by a deacon and sub-deacon, it is called a Pontifical Mass;
2. When it is sung by a priest, assisted by a deacon and sub-deacon, it is called a Solemn Mass;
3. When sung by a priest without deacon and sub-deacon, it is called a Missa Cantata or High Mass;
4. When the Mass is only read in a low tone it is called a low or private Mass.
Q. 926. For what end or intention may Mass be offered?
A. Mass may be offered for any end or intention that tends to the honour and glory of God, to the good of the Church or the welfare of man; but never for any object that is bad in itself, or in its aims; neither can it be offered publicly for persons who are not members of the true Church.
Q. 927. Explain what is meant by Requiem, Nuptial and Votive Masses.
A. A Requiem Mass is one said in black vestments and with special prayers for the dead. A Nuptial Mass is one said at the marriage of two Catholics, and it has special prayers for their benefit. A Votive Mass is one said in honour of some particular mystery or saint, on a day not set apart by the Church for the honour of that mystery or saint.
Q. 928. From what may we learn that we are to offer up the Holy Sacrifice with the priest?
A. We may learn that we are to offer up the Holy Sacrifice with the priest from the words used in the Mass itself; for the priest, after offering up the bread and wine for the Sacrifice, turns to the people and says: “Orate Fratres,” etc., which means: “Pray, brethren, that my sacrifice and yours may be acceptable to God the Father Almighty,” and the server answers in our name: “May the Lord receive the sacrifice from thy hands to the praise and glory of His own name, and to our benefit and that of all His Holy Church.”
Q. 929. From what did the custom of making an offering to the priest for saying Mass arise?
A. The custom of making an offering to the priest for saying Mass arose from the old custom of bringing to the priest the bread and wine necessary for the celebration of Mass.
Q. 930. Is it not simony, or the buying of a sacred thing, to offer the priest money for saying Mass for your intention?
A. It is not simony, or the buying of a sacred thing, to offer the priest money for saying Mass for our intention, because the priest does not take the money for the Mass itself, but for the purpose of supplying the things necessary for Mass and for his own support.
Q. 931. Is there any difference between the sacrifice of the Cross and the sacrifice of the Mass?
A. Yes; the manner in which the sacrifice is offered is different. On the Cross Christ really shed His blood and was really slain; in the Mass there is no real shedding of blood nor real death, because Christ can die no more; but the sacrifice of the Mass, through the separate consecration of the bread and the wine, represents His death on the Cross.
Q. 932. What are the chief parts of the Mass?
A. The chief parts of the Mass are:
1. The Offertory, at which the priests offers to God the bread and wine to be changed at the Consecration;
2. The Consecration, at which the substance of the bread and wine are changed into the substance of Christ’s body and blood;
3. The Communion, at which the priest receives into his own body the Holy Eucharist under the appearance of both bread and wine.
Q. 933. At what part of the Mass does the Offertory take place, and what parts of the Mass are said before it?
A. The Offertory takes place immediately after the uncovering of the chalice. The parts of the Mass said before it are: The Introit, Kyrie, Gloria, Prayers, Epistle, Gospel and Creed. The Introit, Prayers, Epistle and Gospel change in each Mass to correspond with the feast celebrated.
Q. 934. What is the part of the Mass called in which the Words of Consecration are found?
A. The part of the Mass in which the words of Consecration are found is called the Canon. This is the most solemn part of the Mass, and is rarely but slightly changed in any Mass.
Q. 935. What follows the Communion of the Mass?
A. Following the Communion of Mass, there are prayers of thanksgiving, the blessing of the people, and the saying of the last Gospel.
Q. 936. What things are necessary for Mass?
A. The things necessary for Mass are:
1. An altar with linen covers, candles, crucifix, altar stone and Mass book;
2. A Chalice with all needed in its use, and bread of flour from wheat and wine from the grape;
3. Vestments for the priest, and
4. An acolyte or server.
Q. 937. What is the altar stone, and of what does it remind us?
A. The altar stone is that part of the altar upon which the priest rests the Chalice during Mass. This stone contains some holy relics sealed up in it by the bishop, and if the altar is of wood this stone is inserted just in front of the Tabernacle. The altar stone reminds us of the early history of the Church, when the martyrs’ tombs were used for altars by the persecuted Christians.
Q. 938. What lesson do we learn from the practice of using martyrs’ tombs for altars?
A. From the practice of using martyrs’ tombs for altars we learn the inconvenience, sufferings and dangers the early Christians willingly underwent for the sake of hearing Mass. Since the Mass is the same now as it was then, we should suffer every inconvenience rather than be absent from Mass on Sundays or holy days.

Q. 939. What things are used with the chalice during Mass?
A. The things used with the chalice during Mass are:
1. The purificator or cloth for wiping the inside;
2. The paten or small silver plate used in handling the host;
3. The pall or white card used for covering the chalice at Mass;
4. The corporal or linen cloth on which the chalice and host rest.
Q. 940. What is the host?
A. The host is the name given to the thin wafer of bread used at Mass. This name is generally applied before and after Consecration to the large particle of bread used by the priest, though the small particles given to the people are also called by the same name.
Q. 941. Are large and small hosts consecrated at every Mass?
A. A large host is consecrated at every Mass, but small hosts are consecrated only at some Masses at which they are to be given to the people or placed in the Tabernacle for the Holy Communion of the faithful.
Q. 942. What vestments does the priest use at Mass and what do they signify?
A. The vestments used by the priest at Mass are:
1. The Amice, a white cloth around the shoulders to signify resistance to temptation;
2. The Alb, a long white garment to signify innocence;
3. The Cincture, a cord about the waist, to signify chastity;
4. The Maniple or hanging vestment on the left arm, to signify penance;
5. The Stole or long vestment about the neck, to signify immortality;
6. The Chasuble or long vestment over all, to signify love and remind the priest, by its cross on front and back, of the Passion of Our Lord.
Q. 943. How many colours of vestments are used, and what do the colours signify?
A. Five colors of vestments are used, namely, white, red, green, violet or purple, and black. White signifies innocence and is used on the feasts of Our Blessed Lord, of the Blessed Virgin, and of some saints. Red signifies love, and is used on the feasts of the Holy Ghost, and of martyrs. Green signifies hope, and is generally used on Sundays from Epiphany to Pentecost. Violet signifies penance, and is used in Lent and Advent. Black signifies sorrow, and is used on Good Friday and at Masses for the dead. Gold is often used for white on great feasts.
Q. 944. What is the Tabernacle and what is the Ciborium?
A. The Tabernacle is the house-shaped part of the altar where the sacred vessels containing the Blessed Sacrament are kept. The Ciborium is the large silver or gold vessel which contains the Blessed Sacrament while in the Tabernacle, and from which the priest gives Holy Communion to the people.
Q. 945. What is the Ostensorium or Monstrance?
A. The Ostensorium or Monstrance is the beautiful wheel-like vessel in which the Blessed Sacrament is exposed and kept during the Benediction.
Q. 946. How should we assist at Mass?
A. We should assist at Mass with great interior recollection and piety and with every outward mark of respect and devotion.
Q. 947. Which is the best manner of hearing Mass?
A. The best manner of hearing Mass is to offer it to God with the priest for the same purpose for which it is said, to meditate on Christ’s sufferings and death, and to go to Holy Communion.
Q. 948. What is important for the proper and respectful hearing of Mass?
A. For the proper and respectful hearing of Mass it is important to be in our place before the priest comes to the altar and not to leave it before the priest leaves the altar. Thus we prevent the confusion and distraction caused by late coming and too early leaving. Standing in the doorways, blocking up passages and disputing about places should, out of respect for the Holy Sacrifice, be most carefully avoided.
Q. 949. What is Benediction of the Blessed Sacrament, and what vestments are used at it?
A. Benediction of the Blessed Sacrament is an act of divine worship in which the Blessed Sacrament, placed in the ostensorium, is exposed for the adoration of the people and is lifted up to bless them. The vestments used at Benediction are: A cope or large silk cloak and a humeral or shoulder veil.
***********

